Introduction
Pharmacology education today is changing. As computer-assisted learning (CAL) and animal simulator software are increasingly being used in pharmacology, students are now able to learn drug responses interactively and ethically.
Softwares such as MyCalPharm mimic real-world experiments using computerized equipment, making intricate laboratory setups a reality as virtual pharmacology lab experiments.
Below are some essential lab instruments—digitally replicated for today's learners through pharmacology simulation software.
Student’s Organ Bath

The Student’s Organ Bath is a primary apparatus used in experimental pharmacology. It consists of a double-walled glass chamber filled with a physiological solution (like Tyrode’s or Krebs), maintained at body temperature.
Isolated tissues, such as guinea pig ileum or rat ileum, are suspended in the solution and exposed to various drugs to observe contractions or relaxations.
Functions:
- Used in dose-response curve (DRC) plotting.
- Used to calculate PD₂ and PA₂ values.
- Facilitates antagonist vs agonist experiments.
- Illustrates tissue sensitivity and drug-receptor interactions
It is used in multiple interactive pharmacology experiments and is one of the most important tool in pharmacology simulation software.
Arterial Cannula
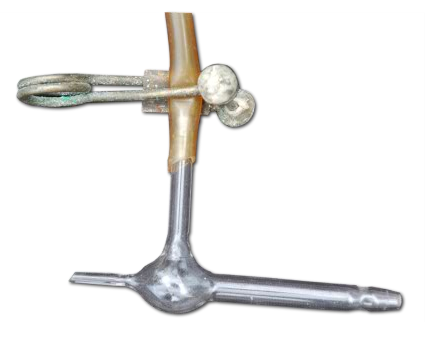
An Arterial Cannula is a small, flexible tube inserted into an artery. In pharmacological experiments, it’s primarily used to introduce drugs into the bloodstream or to record arterial blood pressure. It provides direct access to the circulatory system, allowing real-time monitoring of drug effects on cardiovascular function.
Functions:
- Facilitates drug administration in blood vessels.
- Records blood pressure changes using connected transducers.
- Supports hemodynamic studies.
While real cannulation requires surgical skill, pharmacology lab equipment simulation offers an alternative. MyCalPharm’s animal simulator software mimics the function and outcome of cannulation, enabling students to learn concepts ethically and visually, without performing invasive procedures.
This tool is key to transitioning toward ethical pharmacology education tools.
Pithing Needle

The frog's spinal cord is physically destroyed, typically by inserting a sharp object (such as a pithing needle).
Functions:
- The pointed, sharp tip enables accurate insertion into the frog's skull to reach the brain and spinal cord with minimal external damage.
- Being a metal tool, it can be reused several times after thorough cleaning and sterilization.
Tono Pen

The Tono Pen is a portable tool employed to determine intraocular pressure (IOP)—an extremely important parameter in ophthalmic pharmacology. It's most commonly employed in rabbit eyes in experiments aimed at investigating the effects of various drugs on eye pressure, which plays a key role in investigating treatments for diseases such as glaucoma.
Functions:
- Measures eye pressure quickly and accurately.
- Evaluates ocular drug effectiveness.
- Supports studies on IOP-lowering medications.
Actophotometer

An Actophotometer is an electronic device used to measure the locomotor activity (spontaneous movement) of small laboratory animals such as mice or rats. It operates on the principle of photoelectric cell detection, where movement of the animal interrupts light beams, producing measurable activity counts.
Function:
The primary function of an Actophotometer is to quantify the general activity level or motor behavior of an animal. The instrument consists of a chamber equipped with light sources and photocells on opposite walls. When the animal moves and crosses the light beams, the interruptions are detected by the photocells, and each interruption is recorded as a count of activity.
These activity counts help in:
- Assessing central nervous system (CNS) stimulant or depressant effects of drugs.
- Evaluating sedative, anxiolytic, or stimulant activity in pharmacological studies.
- Monitoring behavioral changes in response to experimental interventions.
Elevated Plus Maze

The Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) is an experimental apparatus designed to evaluate anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) activity, learning, and memory behavior in small laboratory animals, primarily rodents. It was introduced by Handley and Mitani in 1984. The maze consists of two open arms and two closed arms arranged in a plus (+) shape, elevated above the ground, allowing assessment of the animal’s natural aversion to open, elevated spaces versus enclosed areas.
Function:
The Elevated Plus Maze is primarily used to:
- Assess anxiety levels in rodents based on their preference for open versus closed arms.
- Evaluate the anxiolytic or anxiogenic effects of pharmacological agents.
- Study learning and memory by analyzing the animal’s exploration patterns during repeated trials.
In this apparatus:
- Increased time spent in open arms indicates reduced anxiety (anxiolytic effect).
- Preference for closed arms signifies heightened anxiety (anxiogenic state).
- Additional behavioral parameters such as rearing, head dipping, urination, and defecation provide supplementary insights into the emotional state of the animal.
- With the incorporation of video tracking systems and software-based analysis, the EPM now allows for more precise, objective, and reproducible behavioral measurements.
Kymograph

A Kymograph is a mechanical recording device used to graphically record physiological movements or responses, such as muscle contractions, heartbeats, or respiratory movements, in experimental studies. It consists of a rotating drum (known as Sherrington’s revolving drum) on which smoked paper is fixed. The movement of a lever, connected to an isolated tissue or organ, is inscribed on the smoked paper at a controlled speed as the drum rotates. The use of a kymograph in pharmacology plays a vital role in understanding tissue responses to various drugs.
Function:
The primary function of a Kymograph is to record and analyze mechanical or physiological movements of isolated tissues or organs in response to various stimuli or drugs.
During an experiment:
- The lever attached to the isolated tissue (e.g., muscle or heart) moves according to the contractions or relaxations of the tissue.
- These movements are traced as a continuous line on the soot-coated paper mounted on the drum.
- After recording, the soot layer is fixed using a colophony-alcohol-glycerin solution to preserve the tracing permanently.
- This device is extensively used in pharmacology and physiology laboratories for studying:
- Drug effects on isolated tissues.
- Muscle or cardiac responses to stimuli.
- Quantitative measurement of biological responses over time.
Rotarod apparatus

The Rota-Rod Apparatus is a laboratory instrument used to evaluate motor coordination, balance, and grip strength in small laboratory animals such as mice or rats. It consists of a horizontal grooved rod that rotates at a controlled speed, and animals are required to maintain their balance on the rotating rod. The apparatus is widely used in neuropharmacological and toxicological studies to assess the effects of drugs or neurological impairments on motor performance.
Function:
The primary function of the Rota-Rod apparatus is to measure motor coordination, muscle strength, and balance in experimental animals.
During the experiment:
- The animal is placed on the rotating rod.
- Depending on its motor coordination and central nervous system (CNS) activity, the animal attempts to stay balanced on the rod.
- When the animal falls, the sensor-equipped platform beneath the compartment detects the fall, stopping the timer and recording the latency to fall (time spent on the rod).
This data is used to:
- Evaluate the effects of CNS depressants or stimulants on motor activity.
- Assess neuromuscular function and motor learning ability.
- Determine drug-induced impairment or improvement in motor coordination.
Conclusion
With the development of pharmacology simulation software, it is no longer necessary for students to depend exclusively on real-time animal experiments. Software such as MyCalPharm offers virtual pharmacology practicals, where students can conduct interactive pharmacology experiments from any location, without causing harm to animals.
By recognizing how these tools function—and how they are modeled—students can close the gap between conventional laboratory setups and morally acceptable, technology-based pharmacology education.
If you are an educator, student, or institution seeking to get in line with contemporary standards, it's now time to investigate animal simulator software and make the transition toward ethical pharmacology teaching instruments.
